Toxic
Metals | Result | Explanation |
|---|
| Cadmium | High Normal | The level is high normal.Cadmium is a pollutant that is mainly ingested from food and drinking water, and was the cause of the disease known as Itai-Itai disease. It gradually accumulates with age, with most of it being stored in the kidneys. There have also been reports of cadmium being found in high levels in secondhand smoke, raising concerns about the health effects of passive smoking. Additionally, animal studies have reported an increase in cadmium absorption in cases of iron deficiency. To mitigate toxicity of cadmium, it is recommended to consume foods rich in zinc (oysters, red meat, egg yolks, cheese), selenium (seafood, egg yolks, liver), vitamin D (fish, shiitake and other mushrooms, egg yolks), and vitamin C (leafy green vegetables, fruits). |
|---|
| Mercury | Normal | Within the normal range. Mercury is a causative substance for Minamata disease and Niigata Minamata disease, and tends to gradually accumulate with age. Mercury we mainly ingest is methylmercury, which is often found in large fish. Even if the level of mercury is within the standard range, if you are planning to become pregnant, it is suggested that you aim to keep your hair mercury concentration below 2500ppb. |
|---|
| Lead | Normal | Within the normal range. Lead is mainly ingested from food and water and accumulates in the body. Lead easily combines with sulfur in the body and can potentially cause various health problems in the brain, nervous system, hematopoietic system, kidneys, etc. Particularly, small children and pregnant women are considered to be at high risk of health damage from lead. In addition, a dissolution of lead from toys, cooking utensils, and pottery may pose a health risk. |
|---|
| Arsenic | High Normal | The level is high normal.Toxicity of arsenic varies greatly depending on its chemical form, with inorganic arsenic being more toxic than organic arsenic. To reduce the effects of arsenic, it is recommended to consume foods high in selenium (such as seafood, egg yolks, and liver), vitamin D (found in fish, mushrooms like shiitake and maitake, and egg yolks), and vitamin C (found in green and yellow vegetables and fruits). |
|---|
| Aluminum | High Normal | The level is high normal.Aluminum is mostly ingested through food. Its association with Alzheimer's disease has been reported and has received attention, but it cannot be said that ingestion of aluminum is the cause of Alzheimer's disease at this point. Aluminum is relatively abundant in tea leaves, but the toxic form of aluminum (Al3+) does not exist in tea leaves or in the extracted liquid. Processed foods contain more aluminum than unprocessed foods, so be careful if you have any concerns. Aluminum-free baking powder is being developed as a substitute for baking powder containing aluminum, as some children ingest a lot of it from sweets. Since dynamics of aluminum in the body are not clearly understood, further research is expected going forward. |
|---|
| Beryllium | High | Beryllium is used in various industries and everyday products, and it is released into the atmosphere through the combustion of fossil fuels. It is regulated as a hazardous air pollutant under air pollution prevention laws. The most common health effects associated with excessive exposure to beryllium in the workplace include immune reactions known as beryllium sensitization, chronic beryllium disease (CBD), and lung cancer. |
|---|

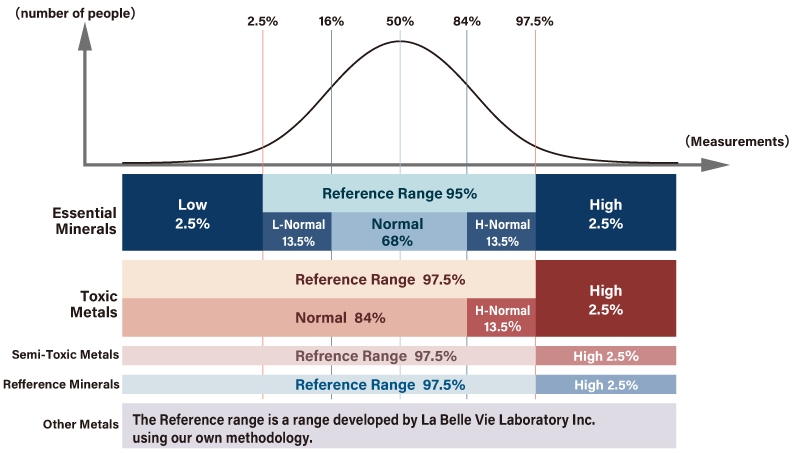
Phosphorus,Selenium,Iron,Sodium,Molybdenum,Copper is outside the standard range.Essential minerals are neither too high nor too low.Make sure to eat a well-balanced diet, exercise moderately, and get enough sleep.
【Toxic Metals / Semi-Toxic Metals】
Cadmium,Arsenic,Aluminum,Beryllium is high.Try to avoid sources of pollution around you to promote detoxification and excretion of toxic metals.If toxic metals are high, it may be due to what you eat, drink, or use on a daily basis or your living environment.
Cadmium: tobacco, rice etc.
Arsenic: Rice, well water, seaweed, etc.
Aluminum: Plant-based proteins, aluminum foil, long-used aluminum cookware, antiperspirants, vaccines, etc.
Beryllium: Air pollution, electronic equipment, etc.
【Detoxification and excretion points for toxic metals】
Toxic metals are excreted through urine and feces, so it is important to regulate kidney and liver function and the intestinal environment.The kidneys and intestines are the key to excretion, and the liver is the key to detoxification. Be careful not to consume excessive salt, drink alcohol, or eat too much, and drink plenty of water, oligosaccharides, and dietary fiber. Moderate exercise is important to keep the kidneys, liver, and intestines active.
See the description for details.
The hair mineral analysis is a lifestyle value for the last 3 months.Periodic inspections are recommended to monitor the transition.